Week Three Quiz
The quiz is divided into two sections. The first section contains questions that assess your recall of essential biological facts. The second set of questions asks you to apply your knowledge of material presented to solve clinical or research problems. The questions in the second set are similar to what you will encounter on the self-assessment and qualifier.
Instructions: To check your answer, click on the option you think is correct.
Recall Questions
-
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the first commitment step of glycolysis?
- Hexokinase
- Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
- Aldolase
- Pyruvate kinase
-
In glycolysis, what is the net gain of ATP molecules per molecule of glucose?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 6
-
Which coenzyme is reduced during glycolysis and later used in oxidative phosphorylation?
- NADP+
- NAD+
- FAD
- Coenzyme A
-
What is the fate of pyruvate under anaerobic conditions in muscle cells?
- It is converted to acetyl-CoA.
- It is converted to lactate.
- It enters the citric acid cycle.
- It is converted to ethanol.
-
The Cori cycle allows the liver to produces glucose from which of the following?
- Acetyl-CoA
- Lactate
- Ribose 5-phosphate
- Glycogen
-
Which of the following enzymes is responsible for the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate?
- Glycogen synthase
- Glycogen phosphorylase
- Glucokinase
- Phosphoglucomutase
-
Which of the following hormones stimulates glycogen breakdown in the liver?
- Insulin
- Epinephrine
- Glucagon
- Cortisol
-
Which of the following molecules directly inhibits glycogen phosphorylase in muscle cells?
- Glucose-6-phosphate
- AMP
- ATP
- Calcium
-
In glycogen synthesis, what is the activated form of glucose that is added to the growing glycogen chain?
- Glucose-1-phosphatee
- Glucose-6-phosphate
- UDP-glucose
- Fructose-6-phosphate
-
What enzyme activates glycogen phosphorylase?
- Protein kinase A
- Glycogen synthase kinase
- Phosphoprotein phosphatase
- Phosphorylase kinase
-
Which precursor for gluconeogenesis is produced in muscles during anaerobic respiration?
- Glycerol
- Lactate
- Acetyl-CoA
- Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
-
Which enzyme catalyzes the final step of gluconeogenesis, converting glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose?
- Hexokinase
- Phosphofructokinase-1
- Glucose-6-phosphatase
- Aldolase
-
Which cofactor is required by pyruvate carboxylase during the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate in gluconeogenesis?
- Biotin
- NADH
- FAD
- TPP (Thiamine pyrophosphate)
-
The oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway generates which of the following?
- NADH
- FADH2
- NADPH
- ATP
-
What is the main purpose of NADPH produced in the pentose phosphate pathway?
- ATP synthesis
- Oxidative phosphorylation
- Reductive biosynthesis and maintaining glutathione in its reduced form
- Glycogen synthesis
-
Which of the following tests is used to diagnose an active SARS-CoV-2 infection?
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) test
- ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
- Western blot
- Rapid strep test
-
What is the primary mechanism of action of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19?
- Directly inactivates the virus
- Inhibits viral replication
- Neutralizes toxins produced by the virus
- Stimulates an immune response by translation of the viral spike protein
-
Which of the following is the primary role of the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) in cellular metabolism?
- To produce ATP directly through substrate-level phosphorylation
- To generate high-energy electron carriers for oxidative phosphorylation
- To synthesize glucose from fatty acids
- To catalyze the breakdown of amino acids into ammonia
-
Which coenzyme is essential for the function of the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex?
- Biotin
- Pyridoxal phosphate
- Thiamine
- Vitamin K
-
In the context of the TCA cycle, which molecule is regenerated to continue the cycle after the production of oxaloacetate?
- Acetyl-CoA
- Succinate
- Fumarate
- Isocitrate
-
Which of the following enzymes is a part of the TCA cycle and also plays a role in the electron transport chain?
- Succinate dehydrogenase
- Citrate synthase
- Malate dehydrogenase
- Aconitase
-
Mutations in enzymes that catalyze reactions in the TCA cycle often lead to lactic acidosis. Why do cells produce lactate if pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis?
- Pyruvate is less soluble than lactate
- Lactate is more easily converted to glucose in the liver
- The conversion of pyruvate to lactate generates NAD+
- Cells can more easily convert lactate to fatty acids
-
Which of the following is the primary function of the electron transport chain (ETC) in oxidative phosphorylation?
- Conversion of glucose to pyruvate
- Production of NADH and FADH2 from acetyl-CoA
- Transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, creating a proton gradient
- Direct synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
-
Which of the following molecules is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain?
- NADH
- FADH2
- Oxygen
- Carbon dioxide
-
Which of the following best characterizes a biochemical reaction with positive ΔG in metabolic pathways?
- Never happens
- Generates ATP
- Coupled with reaction that has a negative ΔG
- Don't require enzymes
Show Explanation
Application Questions
-
The following three questions refer to the image below of a cross-section of a peripheral nerve. What best describes the structure seen in the image?
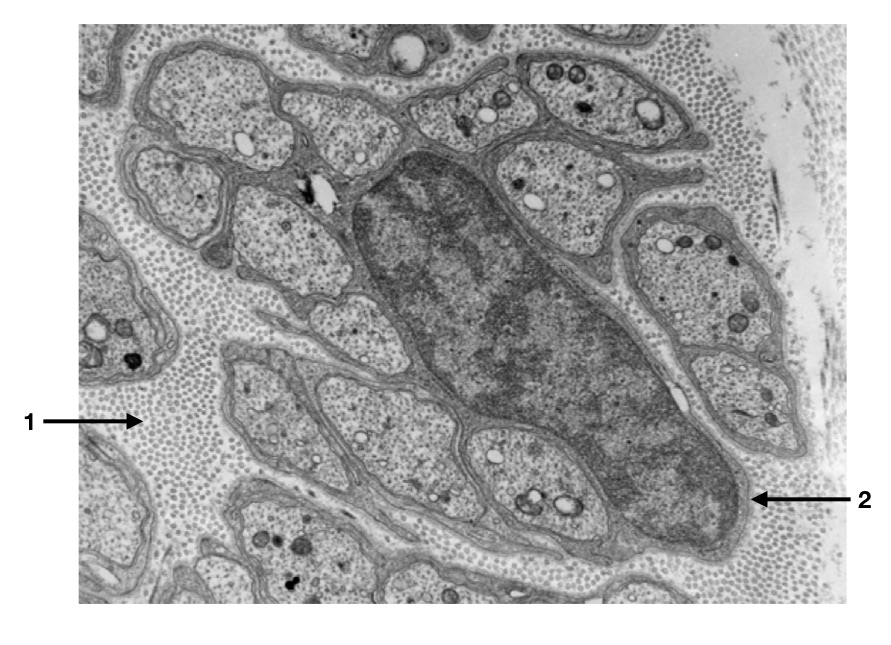
- Myelinated nerve
- Unmyelinated nerve
- Neuron cell body
- Axon terminus
Show Explanation
-
In the image above, what is arrow 1 one pointing to?
- Elastic fibers
- Proteoglycans
- Neuron cell body
- Collagen fibrils
Show Explanation
-
In the image above, what protein would be expect to find in the cell membrane of the region indicated by arrow 2?
- Integrins
- Cadherins
- Claudins
- Connexins
Show Explanation
-
You are studying different muscle tissue and measuring the rate at which each contracts. To initiate contraction, you apply an electrical stimulus to each muscle type. You notice that smooth muscle starts to contract much longer after stimulation than skeletal and cardiac muscle. What accounts for this delayed response in smooth muscle cells?
- Slower rate of myosin activation
- Slower rate of calcium channels opening
- Slower rate of tropomyosin movement
- Slower rate of sodium channels opening
Show Explanation
-
You are working with a neurologist to identify biopsies that show damage to motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscle cells. The biopsies show axons of several different types, and you must quickly identify axons which are most likely part of a motor neuron. Which type would you look for?
- 1 µm diameter, unmyelinated
- 1 µm diameter, myelinated
- 10 µm diameter, myelinated
- 10 µm diameter, unmyelinated
Show Explanation
-
In patients with cystic fibrosis, the concentration of sodium in their sweat higher than normal. What explains the inability of the epithelium in the sweat gland to absorb sodium?
- Reduced activity of the sodium-potassium pump
- Fewer sodium channels in apical membrane
- Depolarization of apical membrane
- More restrictive tight junctions
Show Explanation
-
A patient presents with muscle weakness and cramps. Physical exam finds an arrhythmia. Blood tests show an elevated potassium concentration. What best explains the patient's muscle weakness?
- Hyperpolarization of membrane potential
- Inactivated sodium channels
- Inactivated potssium channels
- Increase in threshold potential
Show Explanation
-
A 40 year old male who weighs 75 kg has a serum sodium concentration of 190 meq/L. What is the water deficit in the patient?
- 8 liters
- 10 liters
- 12 liters
- 16 liters
Show Explanation